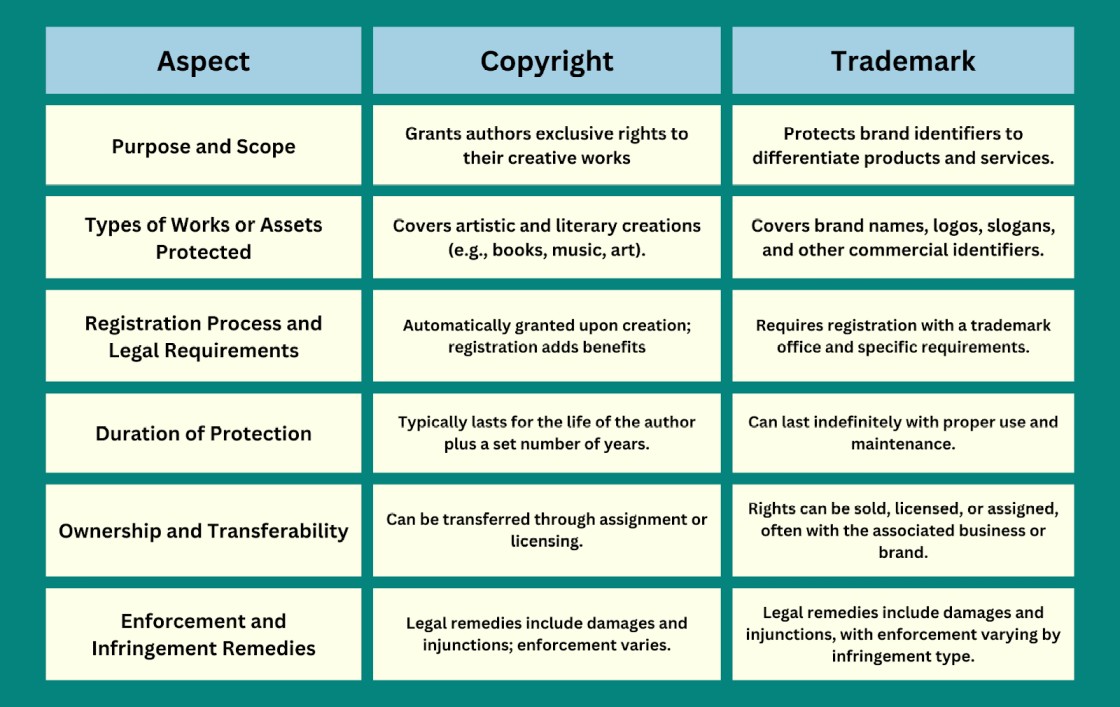
Copyright and trademark protect intellectual property. They serve different purposes.
Understanding these differences is crucial. In the world of intellectual property, copyright and trademark are two distinct protections. Copyright safeguards original works like books, music, and art. Trademark, on the other hand, protects brand identifiers like logos and slogans. Knowing the key legal differences between copyright and trademark helps businesses and creators secure their rights.
This knowledge ensures that creative works and brand identities receive the proper legal protection. Let’s dive into the unique aspects of each type of protection and understand how they differ.
Introduction To Intellectual Property
Intellectual property includes ideas, inventions, and creative work. It protects the rights of creators. There are different types like copyright and trademark. Copyright covers books, songs, and films. Trademarks cover logos, names, and symbols.
Intellectual property is crucial for businesses. It safeguards unique products and services. This protection helps maintain a company’s identity. It also prevents others from using their creations. This boosts trust and brand recognition.

Credit: execedonline.law.columbia.edu
What Is Copyright?
Copyright is a legal right. It protects original works of authorship. These works can be literary, dramatic, musical, or artistic. It gives the creator exclusive rights. They can reproduce, distribute, and display their work. It also includes the right to make derivatives. Copyright lasts for a limited time. After that, the work enters the public domain.
Many types of works are protected by copyright. These include books, poems, and plays. Movies and songs are also protected. Paintings and sculptures fall under copyright too. Even software and websites can be copyrighted. The work must be original and fixed in a tangible form. This means it must be written down or recorded.
What Is Trademark?
A trademark is a unique symbol or word. It identifies a product or service. The scope includes names, logos, and slogans. It can be a single word or a combination.
There are several types of marks:
- Word Marks: Simple words or phrases.
- Design Marks: Logos or images.
- Sound Marks: Unique sounds.
- Color Marks: Specific color used in a product.
- Shape Marks: Unique shapes of products.
All these marks protect brands. They help maintain brand identity.
Credit: zoviz.com
Legal Protections Of Copyright
Copyrights last a long time. For most works, they last the author’s life plus 70 years. After that, the work enters the public domain. No renewal is needed. This long duration helps authors protect their creations.
Copyright infringement occurs when someone uses your work without permission. This can lead to legal action. Courts can issue fines or order the infringer to stop. Authors can also seek compensation. Protecting your work is important.
Legal Protections Of Trademark
A trademark offers protection for a long time. It can last forever with proper renewal. Trademarks usually need renewal every 10 years. This keeps the protection active and strong. Renewal is a simple process but must be done on time. Delays can cause loss of trademark rights. Always keep track of renewal dates.
Trademark owners have rights to stop others from using their marks. This is called infringement. If someone uses your mark, you can take legal action. Enforcement protects your brand and reputation. It’s important to monitor the market for misuse. Quick action helps prevent damage to your business.

Credit: www.hustleinspireshustle.com
Key Differences Between Copyright And Trademark
Copyright protects original works like books, music, and art. These works must be creative and fixed in a tangible form. Trademark protects brand names, logos, and symbols. These marks identify and distinguish products or services in the market.
Copyright protection is automatic once the work is created. Registration is not required but can provide additional benefits. Trademark protection requires registration with the government. This process ensures exclusive rights to the mark.
Case Studies And Examples
One of the most famous copyright cases involved J.K. Rowling. She sued a fan for publishing a Harry Potter encyclopedia. The court ruled in Rowling’s favor. Another famous case involved the song “Blurred Lines”. The creators were sued for copying Marvin Gaye’s music. They lost the case and paid a large fine.
One famous trademark dispute involved Apple and Samsung. Apple claimed Samsung copied their phone designs. The court agreed and Samsung paid damages. Another notable case involved Nike and a small clothing brand. Nike said the brand’s logo looked too similar to their own. The small brand had to change their logo.
Choosing The Right Protection
Think about what you need to protect. Creative works like books, music, and art need copyright. Brand names and logos need trademark.
Consider your business goals. Do you want to protect a logo? You need a trademark. Do you want to protect written content? You need copyright.
Consult a lawyer for detailed advice. They can guide you on which protection suits your needs. Many resources are available online. Government websites offer detailed information.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Main Difference Between Copyright And Trademark?
Copyright protects original works of authorship, like books and music. Trademark protects brand identifiers, like logos and slogans.
Can A Trademark Also Be Copyrighted?
No, trademarks and copyrights are different. Trademarks protect brand identifiers, while copyrights protect creative works.
How Long Does Copyright Protection Last?
Copyright protection typically lasts the lifetime of the author plus 70 years. It varies by country.
Do Trademarks Expire?
Yes, trademarks can expire. They must be renewed periodically, usually every 10 years, to remain valid.
Conclusion
HurryTimer: Invalid campaign ID.Understanding copyright and trademark is essential for protecting your work. Each serves a different purpose. Copyright covers creative works like music, books, and art. Trademarks protect brand names and logos. Knowing the differences helps in safeguarding your rights. Both laws ensure your creations and brands are secure.
Stay informed and make wise decisions. Protect your intellectual property effectively. This knowledge empowers you in the business world.